Hi friends of the Fairywren Project,
To our new followers, welcome! To our continuing followers, sorry it has taken so long to get an update to you! 2021 was a busy year. If you’re short on time we’ll summarize here and expand below:
Update summary:
The Fairywren Project is entering an exciting phase. We’re about 3.5 years old and you’ve submitted over 14,000 eBird checklists! We’re working on your checklist data but in the meantime, we have two research papers we’ve recently finished: one on hybridisation in Fairywrens, and another analyzing the group size data that Allison and I collected during our survey trips in 2018 and 2019. The hybrids paper should be published in the next month or two and the group size paper should hopefully come out in the next six months or so.
2021 was busy, plans for 2022:
I finished my PhD at the end of 2020, then Allison and I spent most of 2021 pursuing research grants to fund field work to supplement the data you are collecting. We see your data as representing the broad, continental patterns occurring in fairywren plumages and group sizes, then we’re hoping to eventually do more focused research that will help us uncover the mechanisms underlying the patterns that your data reveal. Receiving this extra funding is not required for the Fairywren Project to succeed, but it will give us an opportunity to connect the broad scale patterns you are helping to uncover to more fine-scale social processes. In the meantime, I accepted a postdoc position studying Mountain Chickadees in the Sierra Nevada mountains in the U.S. (read more on these fascinating birds here). I’ll be in this position for 2-4 years and during this time, Allison and I will continue our Fairywren Project work while balancing the work required of our research positions. We’re excited for what’s next!
Research coming out soon:
Hybridisation in Fairywrens – if you’re on our email list, you may have seen back in February of last year we sent out a call asking if anyone had ever seen a hybrid fairywren. As teased above in the summary, we’re excited to report that our paper in collaboration with photographers from across the country is now accepted for publication in Australian Field Ornithology, a scientific journal published by Birdlife Australia. This paper documents three new instances of hybridisation in fairywrens and provides further details on a previously-reported fourth instance. The paper should be available in the next month or two. We’ll send a link when it is published so you can learn more about this neat topic. We’ll also update the fairywren hybrids portion of our website at that time.
Group size variation in fairywrens in relation to environmental variation – if you’ve been with us since we launched the project, you might remember that back in 2018 and 2019 Allison and I traveled from southern Victoria north to Broken Hill, NSW, recording fairywren group sizes and plumages along the way. These two trips were our proof-of-concept trips where we were trying out the methods you are using to report group sizes and plumage data. We’re excited to say that these observations turned up some interesting patterns and we’ve now submitted a paper detailing these patterns.
Now that we’ve sent the paper to the journal, an editor at the journal will send the paper to two or three reviewers who will read the paper and give us comments back on it, including whether they agree with our interpretations of the data. This process often takes 2 months or longer, then based on the reviews we’ll have an opportunity to revise the paper and resubmit it. We’re hoping this publication should be out in six months or so. If you cannot wait and want to know the results right away, we’ve posted a pre-print online that you can check out here. This is a pre-publication version of the paper, so it will be revised once we receive reviews, but pre-prints are a common tool to get ideas out quickly, provide access to a wider audience, and get feedback on the research prior to publication.
Next research goals:
Group size variation in fairywrens using your data – our publication of our transect data is a small taste of the data you’ve been submitting on group sizes through your eBird checklists. One of our next projects is to see if the same trends we saw in our transect occur on a continent-wide scale using your checklist data, and to see how these trends vary across species. Allison is currently working on these analyses.
Prevalence of year-round bright plumage in fairywrens – most male fairywrens moult into dull (brown) plumage at the end of the breeding season, however, research by Ana Leitão and colleagues suggested that male Lovely Fairywrens keep bright plumage year-round. It is also recognized that in multiple other species of fairywrens, old males sometimes remain in ornamented plumage year-round, but it appears they are not able to do this for multiple years in a row. However, these observations only come from single study sites, or at most a few populations per species. One of the next questions we’re hoping to answer is: is year-round bright plumage a widespread phenomenon?
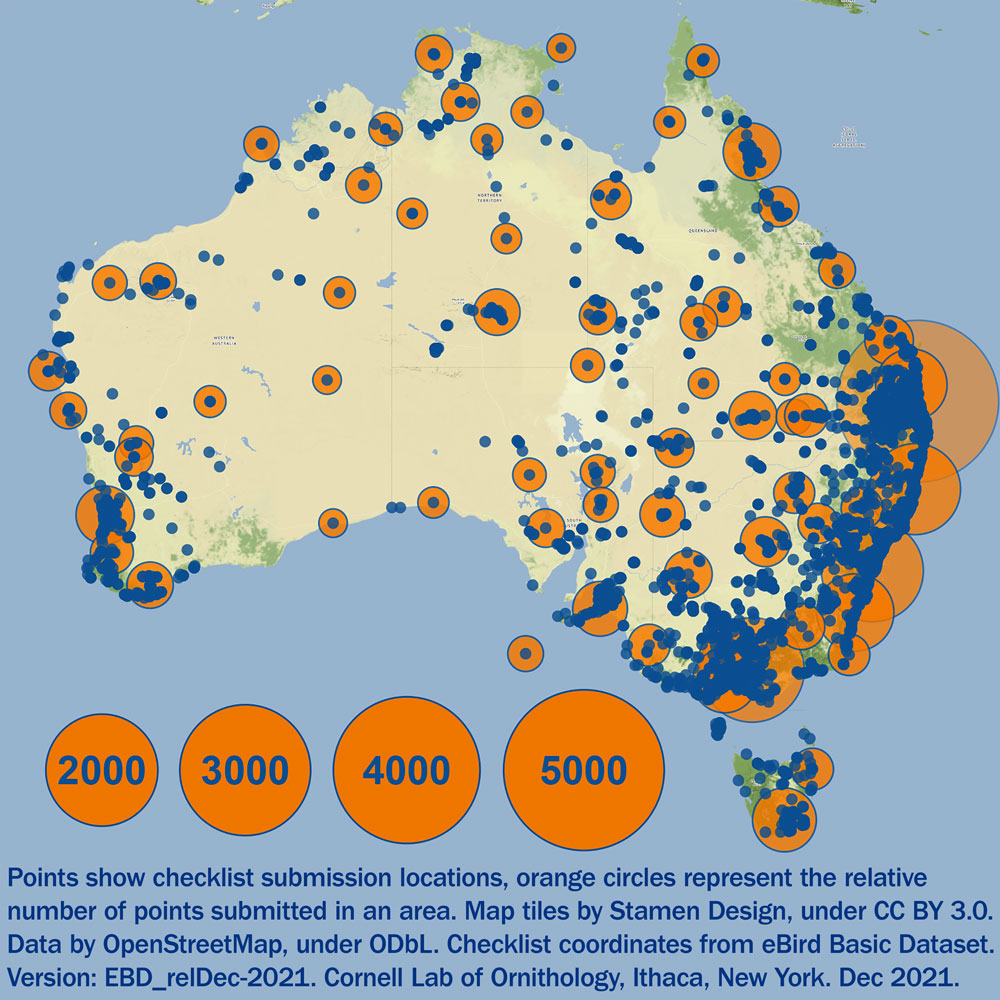
Based on previous research, we only expect a few males in each population to do this each year, but the data you’ve been submitting over the last couple years offer an incredible opportunity to answer this question. Just think if one researcher were to try to answer this question alone, it might make for a fun trip, but it would be impossible to visit as many populations as you have provided data on! Just look at the map below to see how extensive your data are. We expect that year-round bright plumage will be a widespread phenomenon, at least for a couple males in each population each year. However, if it’s not that will be a very interesting result too. Either way, we’re looking forward to seeing what your data show and we’ll keep you updated. And keep submitting data when you can! Observations you submit now through August 2022 (the approximate start of the next breeding season) will likely make it into the final version of this paper.
A further note on funding:
Sometimes participants ask us if they can contribute financially to the Fairywren Project. For those that have asked, thank you for your generosity. However, we always redirect these offers because we don’t think this is a project that can be supported by participant donations alone. Our primary source of support comes from large granting agencies.
Instead, if you want to contribute financially to bird research, consider donating to Birdlife Australia. They’re a great conservation and research organization and the number one advocate for birds in Australia. Also consider a project called Wing Threads, they are currently raising money through around March 8th to fund a ultralight trip around Australia highlighting the plight of shorebirds. For us, just send us your plumage and group size observations via eBird!
A note on data quality:
Almost all of you are submitting observations that are easily interpretable and high quality, but a few participants appear to be submitting plumage observations using only “male” and “female” codes. Male and female codes alone do not give us much information to work with because males can come in multiple plumage types. If you can, either use our suggested codes: bright (b), intermediate (i), dull (d), female (f), juvenile (j), or something similar that is easily interpretable for us. For example, if you say “moulting male” we know that’s an intermediate male, if you say “brown male” we know that’s a dull male. Thanks!
Thank you to everyone who has contributed! Please let us know if you have any questions via fairywrenproject@gmail.com. Look for the link to the paper on hybridisation in fairywrens soon and until then, happy birding!
Joe and Allison
P.S. We hope you're all safe despite the crazy floods on the east coast.